CityHood: An Explainable Travel Recommender System
CityHood is an interactive travel recommender system that suggests cities and neighborhoods based on user preferences. It combines multi-level interest modeling with socio-demographic, cultural, and political data, providing transparent explanations for each recommendation. Accepted for publication at the ASONAM 2025 Demo Track.
CityHood is an interactive and explainable travel recommender system designed to help users discover new cities and neighborhoods that align with their personal preferences. Unlike typical “black-box” recommenders, CityHood provides transparent, feature-rich suggestions by modeling user interests from large-scale data and enriching it with geographic, socio-demographic, political, and cultural indicators. The system integrates an explainable AI technique (LIME) with natural language summaries to ensure users can understand, trust, and engage with the recommendations.
Key Features
- Two-Level Recommendations: Starts with broad city-level suggestions (Core-Based Statistical Areas - CBSAs) and refines them at the neighborhood level (ZIP codes).
- Rich Interest Modeling: Leverages user review patterns from Google Places, contextualized with socio-demographics (income, education), political leaning (2020 U.S. election data), and cultural profiles via Scenes Theory.
- Built-in Explainability: Integrates LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) to show which features influenced a recommendation. These insights are translated into easy-to-understand natural language summaries.
- Interactive UI: A responsive interface built with React and MapLibre allows users to explore maps, label preferences, and inspect the reasoning behind each suggestion.
- Dynamic Content Generation: Neighborhood descriptions are dynamically generated using a local
deepseek-r1:32blarge language model, and visual previews are curated using a hybrid pipeline of computer vision models (Places365 and YOLOv8).
How It Works: A Walkthrough
The user journey is a two-stage process designed for seamless exploration and preference refinement.
Stage 1: City-Level Recommendation
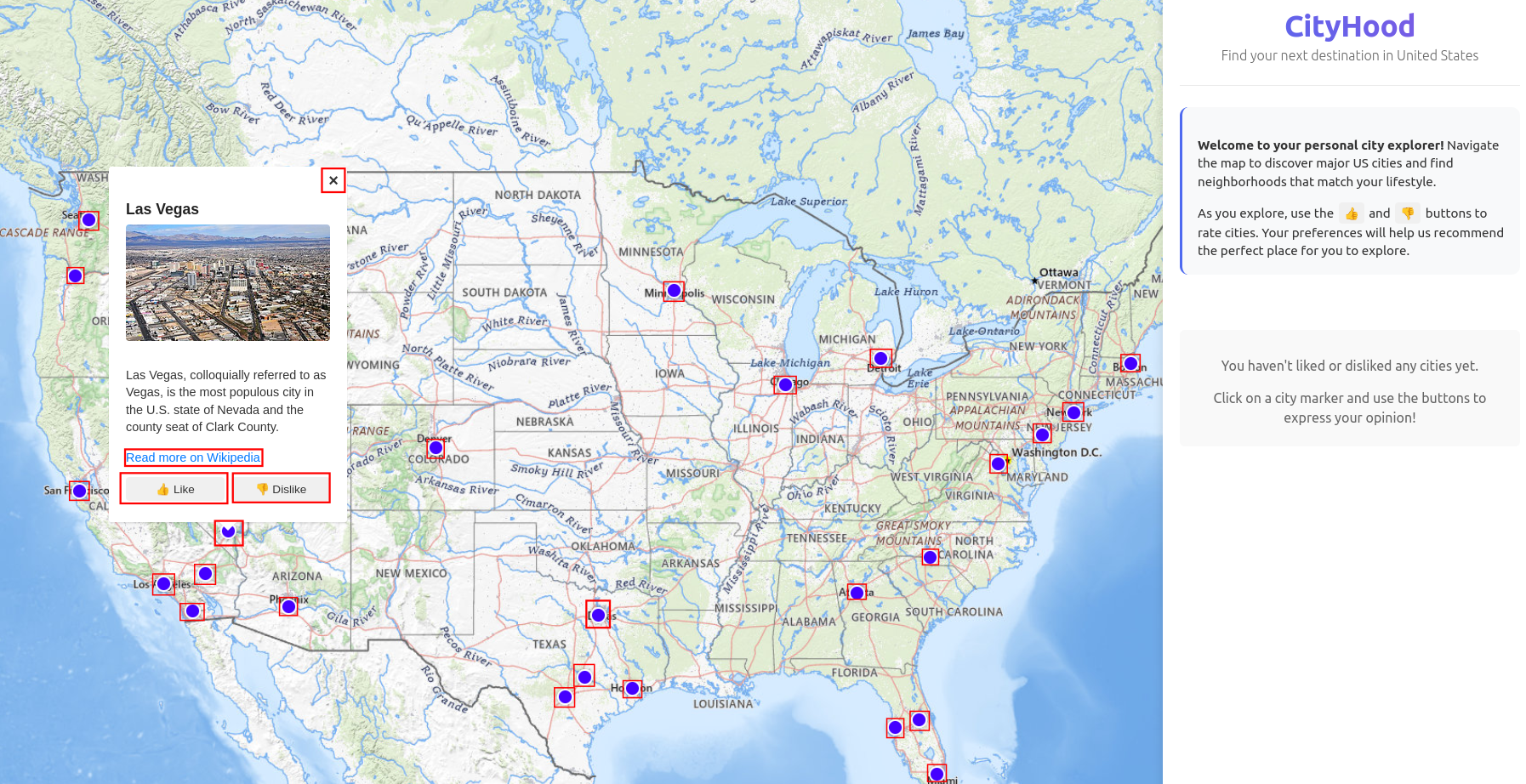
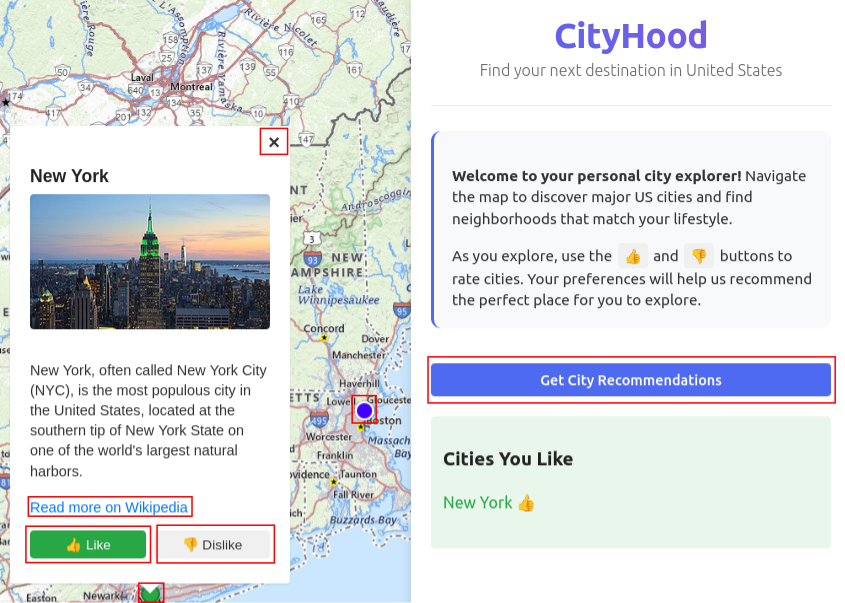
The process begins on a map displaying the most popular U.S. cities (CBSAs). Users can explore cities, view Wikipedia-sourced descriptions, and label them as “liked” or “disliked.” After selecting at least one city, the system generates personalized recommendations.
 |
|---|
| Figure 1(a): Home Screen |
 |  |
|---|---|
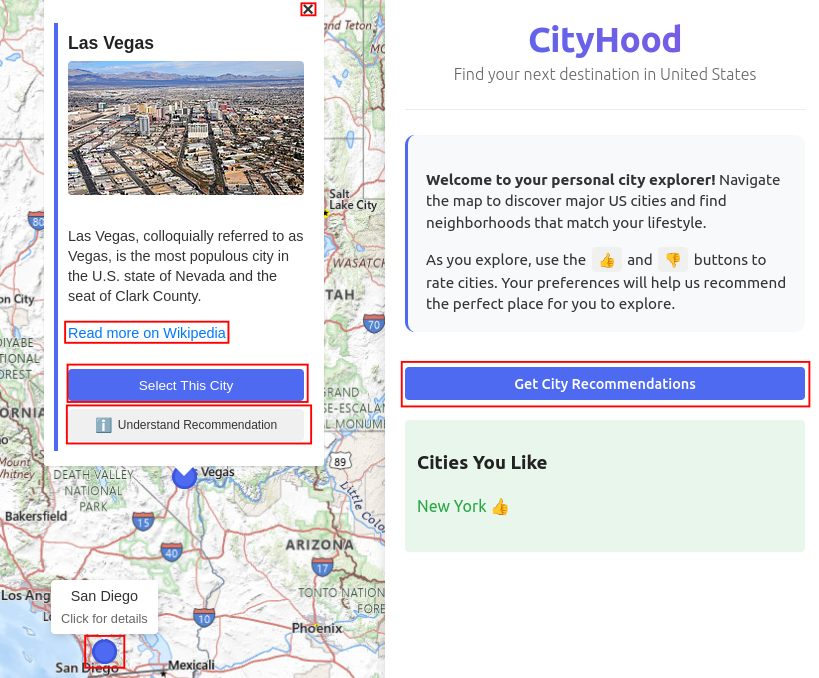
| Figure 1(b): Exploring and Labeling Cities | Figure 1(c): Receiving City Recommendations |
Each recommendation is accompanied by:
- A natural-language explanation justifying the choice.
- Quantitative LIME feature weights and raw similarity scores for full transparency.
Stage 2: Neighborhood-Level Refinement
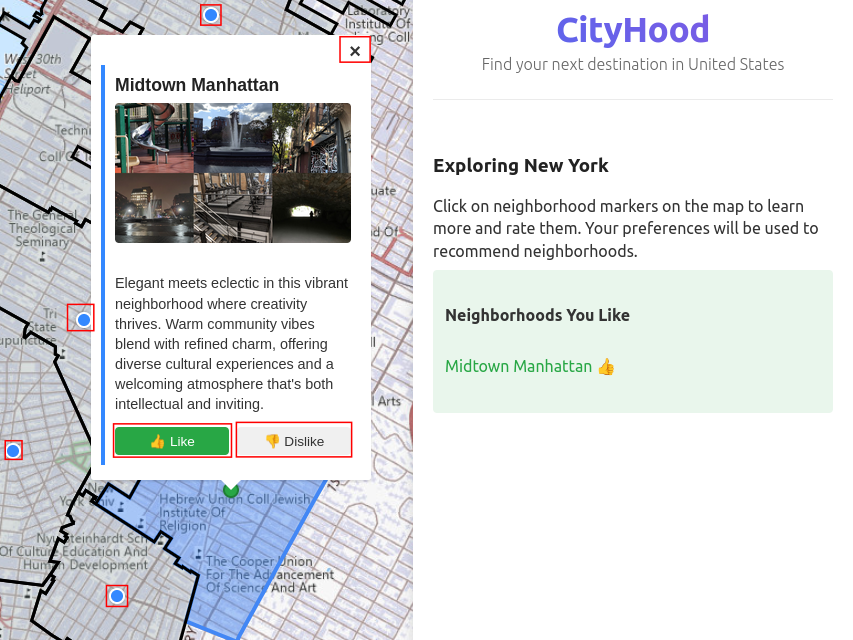
After selecting a recommended city (e.g., Las Vegas), the user refines their preferences at the neighborhood level. The system presents the 10 most popular ZIP codes from the user’s previously liked cities (e.g., New York), which they can then label. Based on these new inputs, CityHood recommends specific neighborhoods in the destination city.
 | 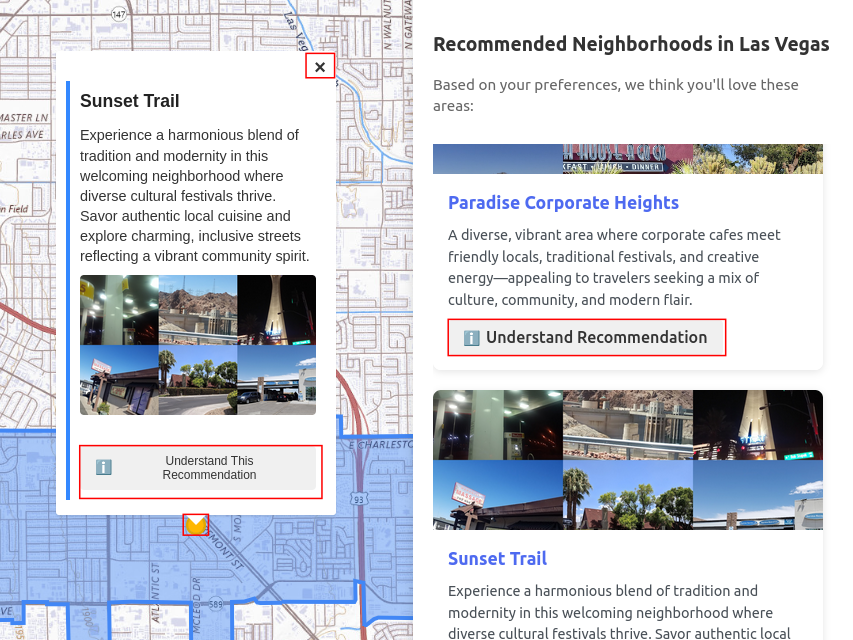 |
|---|---|
| Figure 2(a): Exploring Neighborhoods in a Liked City | Figure 2(b): Recommended Neighborhoods in Destination City |
Technical Deep Dive
Dataset and Features
The system is built on a large-scale dataset of over 666 million Google Places reviews from 113 million users. To focus on tourism, we filtered for users who reviewed venues in at least six different CBSAs, resulting in a core dataset of 245 million reviews by 4.6 million users. Each region (CBSA and ZIP code) is enriched with:
- Socio-demographic data from the NHGIS database (e.g., income, race, education).
- Political leaning from 2020 U.S. election data.
- Cultural profiles derived using Scenes Theory.
Model and Performance
A LightGBM binary classifier is trained to predict whether a region will be of high interest to a user based on its similarity to their previously liked and disliked places. The model demonstrates strong performance, consistently outperforming popularity-based and item-based collaborative filtering (ICF) baselines.
- City-Level: Achieved recall scores between 0.66 and 0.79 and F1-scores between 0.56 and 0.65. For instance, at k=2, our model’s recall was 0.79, compared to 0.31 for popularity and 0.63 for ICF.
- Neighborhood-Level: Achieved recall between 0.59 and 0.77 and F1-scores from 0.47 to 0.75.
System Architecture
- Backend: A Dockerized FastAPI server processes user requests and runs the recommendation model.
- Frontend: A highly interactive web application built with React and MapLibre for responsive map rendering and navigation.
- Explainability: LIME explains individual predictions, and a local LLM generates natural-language summaries from LIME’s feature weights.
Challenges and Solutions
A major challenge was the lack of structured, descriptive data for ZIP codes. We solved this with a custom two-step process to generate dynamic neighborhood summaries:
- Feature Extraction: Regional features used by the model (demographics, culture, etc.) were extracted.
- Text Generation: A local large language model (
deepseek-r1:32b) was prompted with these features to generate coherent, human-readable descriptions.
Similarly, to provide relevant visual context, we developed a hybrid image curation strategy:
- Scene Filtering: Images from reviews are first filtered using the Places365 scene classifier to prioritize outdoor scenes that reflect a neighborhood’s character.
- Object Detection: A lightweight YOLOv8 nano model then filters out images where people (e.g., selfies) or vehicles are the primary subject, ensuring the visuals represent the environment.
Future Work
Our future plans aim to enhance the system’s scope and intelligence:
- Expand geographic coverage beyond the U.S. to global cities.
- Integrate time-aware factors (e.g., trip duration, seasonality).
- Incorporate user intent (e.g., leisure vs. business travel).
- Explore additional location-based social networks (LBSNs) to reduce potential data bias.
Paper
📄 Accepted for publication in the Demo Track at ASONAM 2025.
Title: CityHood: An Explainable Travel Recommender System for Cities and Neighborhoods
Authors: Gustavo H. Santos, Myriam Delgado, Daniel Silver, and Thiago H. Silva
[PDF coming soon]